CAN is an abbreviation of Controller Area Network (CAN). It was developed by German BOSCH company, which is famous for R&D and production of automotive electronic products. It eventually became an international standard (ISO11898). It is the most widely used field bus in the world. one. In North America and Western Europe, the CAN bus protocol has become the standard bus for automotive computer control systems and embedded industrial control local area networks, and has the J1939 protocol designed specifically for large-scale trucks and heavy industrial machinery vehicles using CAN as the underlying protocol.
CAN bus features(1) It is a kind of multi-master bus, that is, each node can become the host, and the nodes can also communicate with each other.
(2) The communication medium can be twisted pair, coaxial cable or optical fiber, and the communication rate can reach 1 mb/s.
(3) The can bus communication interface integrates the physical layer and data link layer functions of the can protocol to complete the framing processing of communication data, including bit stuffing, data block coding, cyclic redundancy check, priority discrimination, etc. Work.
(4) The most important feature of the can protocol is that the traditional station address code is abolished and rain is used to encode the communication data block. The advantage of this method is that the number of nodes in the network is theoretically unlimited, and the identification code of the data block can be composed of 11-bit or 29-bit binary numbers, so 211 or 229 different data blocks can be defined. The data block coding method can also enable different nodes to receive the same data at the same time, which is very important in step-by-step control.
(5) The length of the data segment is up to 8 bytes, which can meet the general requirements of control commands, working conditions and test data in the general industry. At the same time, 8 bytes do not occupy the bus for too long, which verifies the real-time nature of the communication.
(6) The can protocol uses crc check and can provide corresponding error handling functions to ensure the reliability of data communication. The can bus has the outstanding performance, the extremely high reliability and the unique design, is especially suitable for the industry to set up every control unit interconnection. Therefore, it is highly valued by the industry and has been recognized as one of the most promising fieldbuses.
How CAN bus works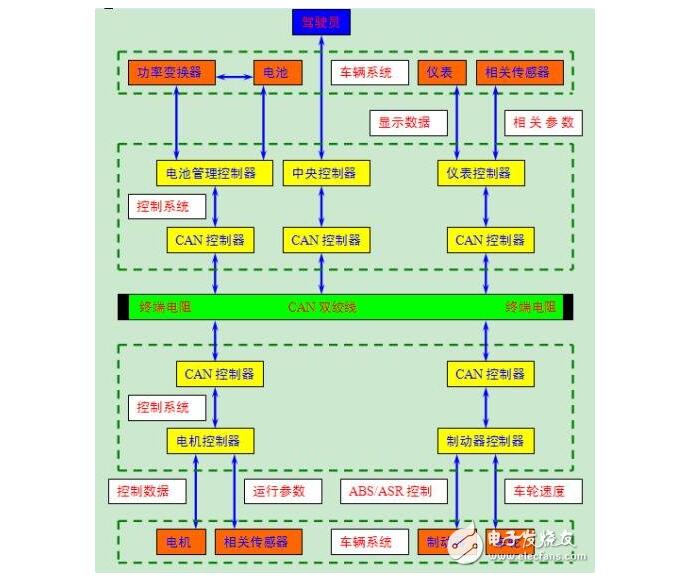
The CAN bus uses serial data transmission. It can operate on a 40m twisted pair at a rate of 1Mb/s, or it can be connected using an optical cable. The bus protocol supports multiple master controllers on this bus. CAN is very similar to the I2C bus in many details, but there are some obvious differences.
When a node (station) on the CAN bus transmits data, it broadcasts it to all nodes in the network in the form of a message. For each node, it receives data regardless of whether it is sent to itself. The 11-characters at the beginning of each message are identifiers that define the priority of the message. This message format is called a content-oriented addressing scheme. In the same system, the identifier is unique and it is not possible for two stations to send a message with the same identifier. This configuration is important when several stations simultaneously compete for bus reads.
When a station wants to send data to other stations, the CPU of the station transmits the data to be sent and its own identifier to the CAN chip of the station, and is in the ready state; when it receives the bus allocation, it transfers to send the message. status. The CAN chip sends the data according to the protocol and forms a certain message format. At this time, other stations on the network are in receiving state. Each station in the receiving state detects the received message and judges whether these messages are sent to itself to determine whether to receive it.
Since the CAN bus is a content-oriented addressing scheme, it is easy to establish a high-level control system and configure it flexibly. We can easily add new stations to the CAN bus without making changes in hardware or software. When the new station provided is a pure data receiving device, the data transmission protocol does not require that the independent portion have a physical destination address. It allows the distribution process to be synchronized, that is, when the controller on the bus needs to measure data, it can be obtained on the Internet without having each controller have its own independent sensor.
The advantages of CAN busâ— It has the advantages of strong real-time performance, long transmission distance, strong immunity to electromagnetic interference, and low cost;
â— It adopts two-wire serial communication mode, which has strong error detection capability and can work in high noise interference environment.
â— With priority and arbitration functions, multiple control modules are connected to the CAN-bus through the CAN controller to form a multi-host local network.
â— It can decide whether to receive or block the message based on the ID of the message.
â— Reliable error handling and error detection mechanisms;
â— After the information sent is destroyed, it can be re-issued automatically;
â— The node has the function of automatically exiting the bus in case of serious errors;
â— The message does not include the source or destination address. Only the identifier is used to indicate the function information and priority information.
CAN bus shortcomings 1) InconsistentThere is a well-known Last-But-One-Bit error in the CAN bus. The CAN bus 2 OA specifies in the message authentication (MessageValidaTIon) that the range of error detection by the sender can be overwritten to the end of the frame. If an error is found, it is retransmitted later according to the rules of priority and state; the range of error detection of the connector covers the frame. The previous one. Therefore, if due to spatial interference, power supply fluctuations and other reasons, for the second-to-last digit of the frame, some of the nodes A consider that there is no error, and some of the nodes B believe that there is something wrong, that is, a so-called ByzanTIne error occurs. At this time, the root EOF should be 7 recessive bits, and Node B thinks this is a form error, so it starts an error frame, instructs the sender to retransmit, and discards the received frame. It is considered that the misconfigured node A receives this frame because only the second-to-last bit is found. If the retransmission of B's ​​notification before the transmitter's next routine transmission is successful, A will receive a repeat frame; if the retransmission is unsuccessful, B loses a frame. In the steering and braking systems, different interpretations of the commands by the four wheels may result in reduced performance or other more serious consequences.
2) UnpredictabilityThe CAN bus divides the node status into ErrorAcTIve, Error Passive, and Bus Off. These three states can be converted to each other under certain conditions. There are different delays in the sending of nodes in different states. There are several possibilities for the highest priority message transmission delay: When the node status is ErrorAcTIve, if the bus is idle, send it immediately. When the node status is ErorActive, if other frames are being sent, wait for the message that is being sent to end. Sending after 3 more bits. When the node status is ErrorPassive, it has a request for retransmission due to an error. If there are no other frames to send, wait for 3 bits for transmission and 8 bits for Suspend Transmission. Send; When the node status is Error Passive, if the bus is idle, after the error and other messages are sent, the wait time is related to the length of other frames; when the node status is Bus Off, wait for the status to return to Error Passive or ErrorActive reissue.
When confirming the status of a node, there are several factors that need to be considered: First, the node is shared by the highest priority information and other information. Therefore, errors that occur during the transmission of other information also affect the node status. Second, The conditions for entering the status of ErrorPassive or BusOff are the value of the sending error counter and/or the receiving error counter. Due to the atomic broadcast characteristics of CAN, sending errors or receiving errors of other nodes will open an error frame, thereby affecting the receiving error counter of this node. The value of , which in turn affects the status of the node.
For less priority information, the transmission time is more discrete. In the feedback control system, the large-range jitter of the sampling adjustment period is equivalent to the change after the signal delay, which may cause the system performance to degrade or become unstable. In safety-related open-loop systems, jitter may cause confusion in the sequence of actions.
3) Channel error jamThe node may be temporarily or permanently disabled due to interference or other reasons. The erroneous host commands the CAN transceiver to continuously send a message, the so-called Babbling ldiot error. Since the format of this information is all legal, CAN has no corresponding mechanism to handle this situation. According to CAN's priority mechanism, information lower in priority than it is blocked temporarily or permanently. Since the CAN bus has the above-mentioned fundamental defects, it will pose a great risk in a more stringent control system and cannot meet the requirements of safety, environmental protection, and energy saving. CAN's event-triggered protocol features limit the application, development, and production of ECUs. Not only are used ECUs difficult to reuse, but they are also not conducive to improving and developing new ECUs.
Now, the high performance and reliability of CAN has been recognized, and it is widely used in industrial automation, ships, medical equipment, industrial equipment, etc. Fieldbus is one of the hot spots in the field of automation in today's automation industry and is known as the field of automation. Computer LAN. Its appearance provides powerful technical support for distributed control systems to realize real-time and reliable data communication between various nodes.
CAN bus in the field of industrial control mainly uses low-speed fault-tolerant CAN, that is ISO11898-3 standard, and 500 Kbps high-speed CAN is often used in the automotive field.
A certain imported vehicle owns multiple control networks such as body, comfort, and multimedia. Among them, the body control uses CAN network, the comfortable use of LIN network, the multimedia use of MOST network, the CAN network as the main network, and the control of engine, transmission, ABS, and other body safety. Modules, and share the speed, speed, oil temperature, etc. to the entire vehicle, to achieve intelligent control of the car, such as automatically locking the door at high speed, when the airbag pops up, automatically open the door and other functions.
CAN system is divided into high-speed and low-speed, high-speed CAN system uses hard-line is a power type, speed: 500kbps, control ECU, ABS, etc.; low-speed CAN is comfortable, speed: 125Kbps, the main control instrument, security and so on.
A hospital has five 16T/H XXXX gas boilers, providing 5kg/cm2 of steam to the laundry room, preparation room, supply room, domestic water, and heating facilities. It consumes 12 million m3 of natural gas and consumes 200,000 tons of natural gas in the year. Tap water. The hospital adopts a relay-type heating method to conduct regional management of the heating network and is divided into four major heating areas. The amount of gas used for winter heating is very large. Based on this, a distributed boiler steam heating network intelligent monitoring system based on CAN fieldbus is designed. Field application shows that the building automation system has the characteristics of strong anti-interference ability, easy on-site configuration, high degree of networking, and friendly man-machine interface.
Balancing Head Boards of various types including 2bnds,4bnds head boards,etc, which is specially used for balancing and pulling splited conductors in electric power line transmission project, etc. It is made of high strength steel with small volume, light weight, no-damage to conductors. By high quality steel material and good design, this kind of Conductor Head Boards can be durable and long service life. we are a professional Chinese exporter of Balancing Head Board and we are looking forward to your cooperation.
Yangzhou Qianyuan Electric Equipment Manufacturing & Trade Co. Ltd is specialized in manufacturing and trade of electric power line transmission tools. Our main products are Anti-twisting Steel Wire Rope,Stringing Pulley,Hydraulic Crimping Compressors,Engine Powered Winch,Motorised Winch,Wire Grip,Gin Pole,Cable Stand,Mesh Sock Grips,Cable Conveyor,Lever Chain Hoists and so on,which are mainly supplied to power companies,railroad companies and other industry fields.
All our products are certified by China National Institute.To assure the quality, we will do 100% inspection for raw material, production procedure, packing before shipment,
so we do have the confidence to supply customers with high-quality and high-efficiency products.
"Customer satisfaction" is our marketing purposes,so we have extensive experience in professional sales force,and strongly good pre-sale, after-sale service to clients. We can completely meet with customers' requirements and cooperate with each other perfectly to win the market.Sincerely welcome customers and friends throughout the world to our company,We strive hard to provide customer with high quality products and best service.
head boards, balancing head boards, balancing running boards
Yangzhou Qianyuan Electric Equipment Manufacturing & Trade Co.Ltd , https://www.qypowerline.com
