Basically, the main function of the LED driver is to convert the input AC voltage source into a current source whose output voltage can vary with the forward voltage drop of the LED Vf.
As a key component in LED lighting, the quality of the LED driver directly affects the reliability and stability of the overall luminaire. Based on LED driver and other related technologies and customer application experience, this paper analyzes and analyzes many failures in lamp design and application:
1. The range of variation of the LED lamp bead Vf is not considered, resulting in low efficiency of the lamp and even unstable operation.
The load end of the LED luminaire is generally composed of a number of LEDs connected in parallel, and its working voltage is Vo=Vf*Ns, where Ns represents the number of LEDs connected in series. The Vf of the LED fluctuates with temperature fluctuations. In general, at a constant current, Vf becomes low at high temperatures, and Vf becomes high at low temperatures. Therefore, the LED lamp load voltage corresponds to VoL at high temperature, and the LED lamp load voltage corresponds to VoH at low temperature. When selecting an LED driver, consider that the driver output voltage range is greater than VoL~VoH.
If the maximum output voltage of the selected LED driver is lower than VoH, the maximum power of the luminaire may not reach the actual power required at low temperature. If the lowest voltage of the selected LED driver is higher than VoL, the driver output may exceed the working range at high temperature. Unstable, the lamp will flash and so on.
However, considering the overall cost and efficiency considerations, the ultra-wide output voltage range of the LED driver cannot be pursued: the driver efficiency is the highest because the driver voltage is only in a certain interval. After the range is exceeded, the efficiency and power factor (PF) will be worse, and the driver output voltage range is designed to be too wide, resulting in increased cost and inefficient optimization.
2. Power reserve and derating requirements are not considered
In general, the nominal power of an LED driver is the measured data at rated ambient and rated voltage. Considering that different customers have different applications, most LED driver suppliers will provide power derating curves (common load vs ambient temperature derating curves and load vs. input voltage derating curves) on their own product specifications.
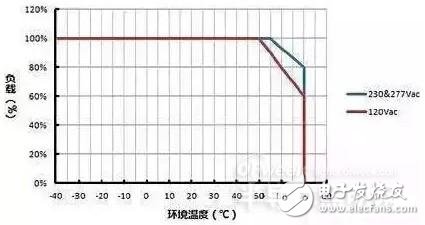
As shown in Figure 1, the red curve shows the power derating curve of the LED driver's load as a function of ambient temperature at 120Vac input. When the ambient temperature is below 50 °C, the drive allows 100% full load. When the ambient temperature is up to 70 °C, the drive can only derate to 60% load. When the ambient temperature changes between 50-70 °C, the drive load will follow. The temperature rises and decreases linearly.
The blue curve shows the power derating curve of the LED driver's load as a function of ambient temperature at 230Vac or 277Vac input. The principle is similar.
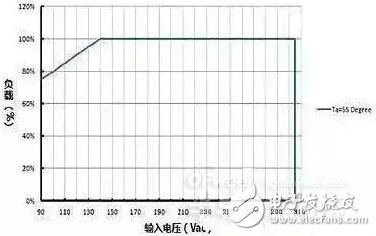
As shown in Figure 2, the blue curve shows the derating curve of the LED driver's output power as a function of input voltage at an ambient temperature of 55 °C. When the input voltage is 140Vac, the load of the driver allows 100% full load, and the input voltage is lowered. If the output power is constant, the input current will rise, resulting in increased input loss, reduced efficiency, and increased device temperature. Individual temperature points will be May exceed the standard and may even cause device failure.
Therefore, as shown in Figure 2, when the input voltage is less than 140Vac, the output load of the driver is required to decrease linearly as the input voltage decreases. After understanding the derating curve and the corresponding requirements, the LED driver should be considered and selected according to the actual ambient temperature and input voltage, and the derating margin should be appropriately set.
3, do not understand the working characteristics of LED
Some customers have requested that the input power of the lamp be a fixed value, fixed by 5% error, and the output current can only be adjusted to the specified power for each lamp. Due to the different working environment temperatures and lighting times, the power of each lamp will vary greatly.
Customers make such requests, despite their marketing and business factor considerations. However, the volt-ampere characteristics of the LED determine that the LED driver is a constant current source, and its output voltage varies with the LED load series voltage Vo. The input power varies with Vo when the overall efficiency of the driver is substantially constant.
At the same time, the overall efficiency of the LED driver will increase after thermal balance. Under the same output power, the input power will decrease compared to the startup time.
Therefore, when the LED driver application needs to formulate the requirements, it should first understand the working characteristics of the LED, avoid introducing some indicators that do not conform to the principle of the working characteristics, and avoid the indicators far exceeding the actual demand, and avoid excessive quality and cost waste.
4, failure in the test
There have been customers who have purchased many brands of LED drivers, but all samples failed during the test. Later, after on-site analysis, the customer used the self-internal regulator to directly supply power to the LED driver. After power-on, the regulator was gradually increased from 0Vac to the rated operating voltage of the LED driver.
Such a test operation makes it easy for the LED driver to start up and load at a small input voltage, which would cause the input current to be much larger than the rated value, and the internal input related devices such as fuses, rectifier bridges, The thermistor or the like fails due to excessive current or overheating, causing the drive to fail.
Therefore, the correct test method is to adjust the voltage regulator to the rated operating voltage range of the LED driver, and then connect the driver to the power-on test.
Of course, technically improving the design can also avoid the failure caused by such test misoperation: setting the startup voltage limiting circuit and the input undervoltage protection circuit at the input of the driver. When the input does not reach the startup voltage set by the driver, the driver does not work; when the input voltage drops to the input undervoltage protection point, the driver enters the protection state.
Therefore, even if the self-recommended regulator is used in the customer test, the drive has self-protection function and will not be invalid. However, customers must carefully understand whether the LED driver products purchased have this protection function before testing (taking into account the actual application environment of the LED driver, most LED drivers do not have this protection function).
5, different loads, different test results
When the LED driver is tested with an LED lamp, the result is normal. When the test is carried out with an electronic load, the result may be abnormal. Usually this phenomenon has the following reasons:
(1) The output voltage or power of the output of the driver exceeds the working range of the electronic load meter. (especially in CV mode, the maximum test power should not exceed 70% of the maximum load power, otherwise the load may be over-power protected during loading, causing the drive to not work or load.)
(2) The characteristics of the electronic load meter used are not suitable for measuring the constant current source. The load voltage position jump occurs, causing the drive to not work or load.
(3) Because the input of the electronic load meter will have a large internal capacitance, the test is equivalent to connecting a large capacitor in parallel with the output of the driver, which may cause unstable current sampling of the driver.
Because the LED driver is designed to meet the operating characteristics of LED luminaires, the closest test to actual and real-world applications should be to use LED bead as the load, string on the ammeter and voltmeter to test.
6. The following conditions that often occur can cause damage to the LED driver :
(1) The AC is connected to the DC output of the driver, causing the drive to fail;
(2) The AC is connected to the input or output of the DC/DC driver, causing the drive to fail;
(3) The constant current output terminal is connected with the modulating light, causing the driver to fail;
(4) The phase line is connected to the ground line, resulting in no output of the driver and charging of the outer casing;
7, the phase line is wrong
Generally, the outdoor engineering application is a 3-phase four-wire system. Taking the national standard as an example, the rated working voltage between each phase line and the neutral line is 220Vac, and the voltage between the phase line and the phase line is 380Vac. If the construction worker connects the input of the drive to the two phase lines, the power input to the LED driver exceeds the standard and the product fails.
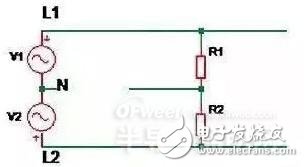
As shown in the figure above, V1 represents the first phase voltage, V2 represents the second phase voltage, and R1 and R2 represent the LED drivers normally installed in the line. When the neutral line (N) on the line is disconnected, the drivers R1 and R2 on the two branches are connected to the 380Vac voltage in series. Because of the difference in input internal resistance, when one of the drivers is charged to start, the internal resistance becomes small, and the voltage may be mostly applied to the other driver, causing its overvoltage damage to fail.
Therefore, it is recommended that the switch or circuit breaker be broken together on the same distribution branch, and not only the neutral line can be disconnected. Do not place the distribution fuse on the neutral line. Avoid contact with the neutral line on the line.
8, the grid fluctuation range is beyond the reasonable range
When the wiring of the same transformer grid branch is too long and there are large power equipment in the branch, when the large equipment starts and stops, the grid voltage will fluctuate drastically, and even the grid will be unstable. When the instantaneous voltage of the power grid exceeds 310Vac, the driver may be damaged (even if there is a lightning protection device, because the lightning protection device is dealing with pulse spikes of several tens of uS levels, and the power grid fluctuation may reach several tens of mS or even several hundred mS).
Therefore, special attention should be paid to the large-scale electric machinery on the street lighting branch network. It is best to monitor the fluctuation range of the power grid or the power supply of the separate grid transformer.
9, the line frequently trips
The lights on the same branch are connected too much, resulting in overloading of the load on one phase and uneven distribution of power between the phases, causing the line to trip frequently.
10, drive cooling
When the drive is installed in a non-ventilated environment, the drive housing should be in contact with the lamp housing as much as possible. If possible, apply thermal grease or thermal pad on the contact surface between the housing and the lamp housing to improve the heat dissipation performance of the driver, thus ensuring the driver's Life and reliability.
In summary, the LED driver has many details to be aware of in practical applications. Many problems need to be analyzed and adjusted in advance to avoid unnecessary failures and losses!
Super Tweeter Bullet,Tweeter Driver,Speakers For Concert Speakers,Speakers For Performances
NINGBO RFUN AUDIO TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.mosensound.com
