The last 3GPP sub-conference in 2017 was held in Reno, USA, from November 27th to December 1st, including RAN185, SA2#124 and other meetings. News from the US 3GPP shows that the first version of the 3GPP 5G NSA is officially frozen, and in June 2018, the SA version will be frozen. China Mobile experts also said that this is the first version of NSA, which means that the first 5G standard of 3GPP has finally come out!
The 5G NR architecture evolution is divided into NSA (non-independent networking) and SA (independent networking). Previously, experts from ZTE, Intel and other industry players said that Rel.15 will complete the standard freeze in December this year, and complete the SA (independent networking) standard freeze in June next year, facing eMBB commercial scenarios. According to the 3GPP's plan, by the end of 2019, the full version of the Rel.16 standard will be completed.
This is the overall rhythm of the standard evolution, and it is also the consensus reached by the industry after many speed increases.
In the development of 5G standards, the power from China played an important role. It is understood that Chinese communication companies contributed 3GPP's proposal on 5G, accounting for 40% of all proposals; Chinese experts also accounted for a large proportion of each 5G working group, for example, in RAN1, as a working group defining 5G physical layer, Chinese Experts accounted for 60%; Chinese and foreign experts serving Chinese communication companies accounted for 40% of the total.
China leads the development of 5G technology
China is a core leader in the 5G era. It has played an important role not only in standards organizations such as 3GPP, but also in the world in terms of technical testing and spectrum demarcation. On the one hand, the IMT-2020 (5G) promotion group led the 5G technology R&D test has completed the second phase of the test, and fully launched the third phase of the test, focusing on product development, verification and industrial synergy before 5G commercial, before commercialization On the other hand, China has released the frequency usage plan for the 5G system in the 3000-5000MHz frequency band (mid-band), becoming the first country in the world to release the frequency usage plan for the 5G system in the mid-band.
In China, the 5G test led by the IMT-2020 (5G) promotion group was launched in January 2016. The first phase mainly completed the key technical verification test. China's 5G two-stage test began in September 2016, and built the world's largest 5G test field to promote the construction of a complete 5G industry chain.
In the case of good results in the second-stage test, Wei Kejun, head of the 5G trial of the IMT-2020 (5G) promotion group, said that in September 2017, the drafting of the test specification for the third phase was fully initiated, and the NSA-based and SA-based The specification of the framework has fully started the construction of the 5G test environment, completed the transmission construction before the end of 2017, and completed the environmental construction in March 2018.
Interpretation of the first 5G international standard report

This report provides an in-depth look at the minimum specifications for 5G. For laymen, it means that 5G cellular devices will allow a single mobile base station to achieve at least 20Gbps downlink speed and 10Gbps uplink speed. This is a theoretical speed for a user. In fact, all users in a cell share 20 Gbps of bandwidth, and 5G can support at least 1 million users per square kilometer.
What does this mean compared to current 4G technology? If you want to download an 8GB HD movie, the 5G network only takes you six seconds. The current 4G LTE takes seven to eight minutes, and the older 3G takes more than an hour.
ITU's approval is the first step towards standardization, and Buonomo said that ITU has more work to do in developing more reports and recommendations to finalize the 5G requirements. “The 5G complete standardization process is likely to end by the end of 2019, and the ITU Recommendations will eventually include all the technical specifications of IMT-2020 (5G),â€
It should be noted that no ICT can be fully standardized on a global scale without the approval of ITU! That is to say, although many technology companies are currently conducting R&D and testing of 5G technologies on their own, these tests actually follow the initial guidelines set by ITU.
In February of this year, the International Telecommunication Union adopted and published the draft IMT-2020 in Geneva, laying the foundation for the subsequent 5G technical specifications of 192 member states. The final version of the documentation is almost unchanged from the draft. Sergio Buonomo, consultant to ITU-R 5 expert group responsible for developing radiocommunication guidelines (including 5G), said: “This is also normal for such high-tech reports.â€
3GPP R15 NSA (5G NR non-independent networking) core standard
This frozen 3GPP R15 NSA (5G NR non-independent networking) core standard part content: that is, 4G core network (EPC) is used, 4G is used as the anchor point of the control plane, and LTE and 5G NR are used for dual connection. The existing LTE network deploys 5G to meet the needs of leading operators to achieve 5G coverage quickly.
For NSA deployments, you can choose between co-site deployment and non-co-site deployment.
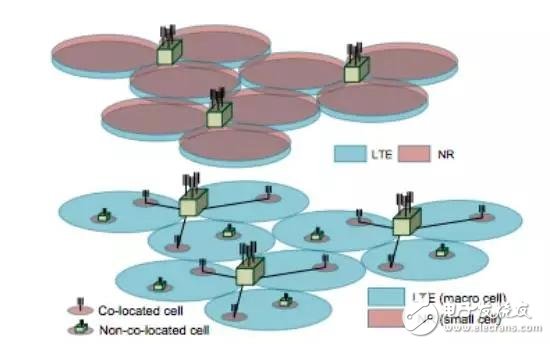
5G base station and 4G base station co-site and non-co-site deployment mode
The 5G base station (gNB) can also be used as a micro-station, and can be deployed together with an existing LTE base station (eNB) or non-co-site to solve indoor or hotspot coverage.
For 5G networking, 3GPP proposed 12 networking options by Deutsche Telekom at the Busan conference last year. Among them, options 3/3a/3x, 7/7a/7x, and 4/4a are non-independent networking architectures, and options 2 and 5 are independent networking architectures.
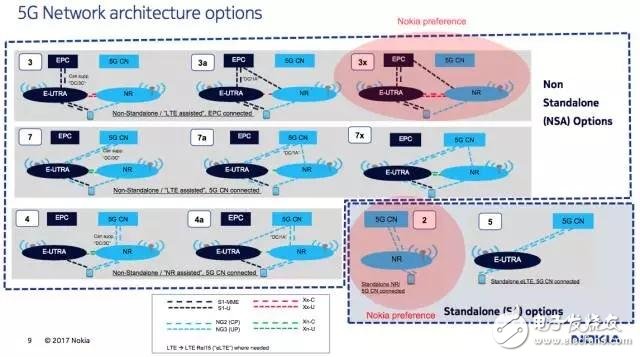
Picture from NOKIA
In short, non-independent networking is divided into three phases:
1) The 4G base station (eNB) and the 5G base station (gNB) share the 4G core network (EPC), the eNB is the master station, the gNB is the slave station, and the control plane signaling goes to the 4G channel to the EPC.
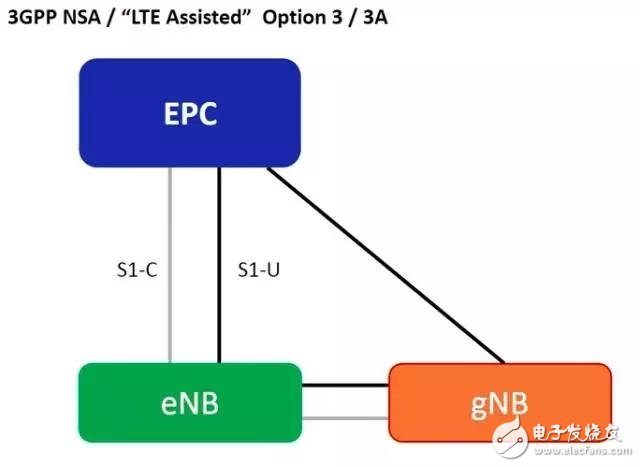
The advantage is that there is no need to add a 5G core network (NGCN), which is beneficial for operators to quickly deploy 5G using the existing 4G network infrastructure to seize coverage and hotspots.
However, since 5G signaling goes all the way to the 4G channel, there is a risk of overloading the 4G core network signaling. Therefore, this stage mainly solves the initial 5G coverage.
2) The 4G base station (eNB) and the 5G base station (gNB) share the 5G core network (NGCN), the eNB is still the master station, the gNB is the slave station, and the control plane signaling goes from the 4G base station to the 5G core network.
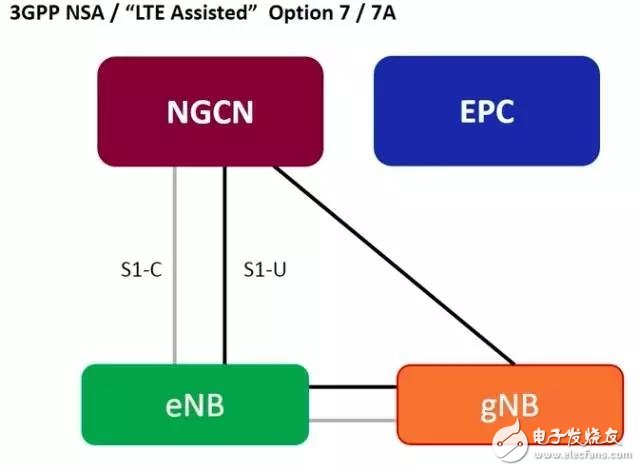
At this stage, the 5G core network replaces the 4G core network, which solves the risk of overloading the core network signaling. Therefore, it mainly addresses the 5G capacity requirement.
3) The 4G base station (eNB) and the 5G base station (gNB) share a 5G core network (NGCN), the gNB is a master station, and the eNB is a slave station.
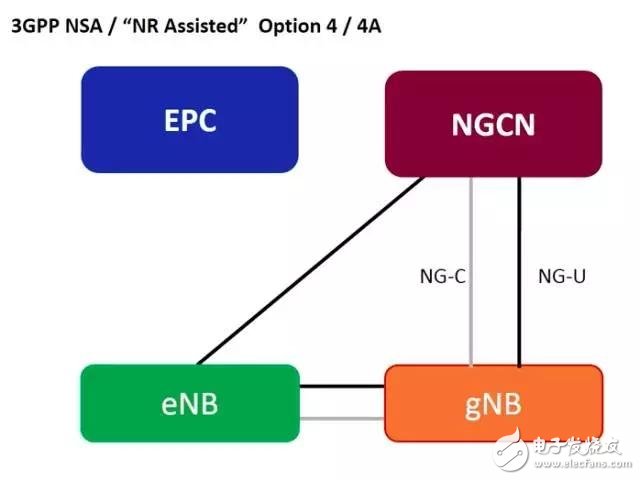
This stage is not only for 5G enhanced mobile broadband scenarios, but also for large-scale Internet of Things and low-latency and high-reliability Internet of Things. In short, it is a diversified business for 5G in the era of universal connectivity.
It is worth mentioning that the concept of dual connectivity (DC) is not new about LTE and NR dual connectivity. The dual connectivity between LTE base stations was introduced in 3GPP R12, which was completed in March 2015, in 2016. A similar dual connectivity aggregation technique for LTE and WLAN is also introduced in 3GPP R13 completed in the month.
However, this is the first time that dual connectivity between two different generations of 3GPP wireless technologies.
Since the underlying technologies of LTE and NR are not the same, there are many challenges that need to be overcome and solved. For example, in order to establish and modify dual connectivity operations, the handset must understand both LTE and NR RRC control signaling.
In short, the first standard of 5G is favorable for the early implementation of 5G commercial use by leading operators. From 2G to the current 5G, the pace of updating is getting faster and faster.
Iphone Screen Protector,Tempered Glass,Privacy Tempered Glass,Hydrogel Screen
Shenzhen TUOLI Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szhydrogelprotector.com
