Sinusoidal alternating current refers to the current (or voltage) whose magnitude and direction change periodically according to the sinusoidal law over time, also called simple harmonic alternating current. The electricity we use every day is sinusoidal alternating current, which is the most basic and important of various forms of alternating current.
In a DC circuit, the magnitude and direction of the voltage or current do not change with time, but in an AC circuit, the magnitude or direction of the voltage or current changes with time, and its changing laws are diverse, and the most common applications are It is alternating current that changes according to the sine law.
Three elements of sinusoidal alternating currentA sine AC electric energy is completely determined, and it is the only sine quantity. As long as you know the maximum value, angular frequency and initial phase, you can write its mathematical expression and draw its waveform diagram, so put these three These physical quantities are called the three elements of sinusoidal alternating current.
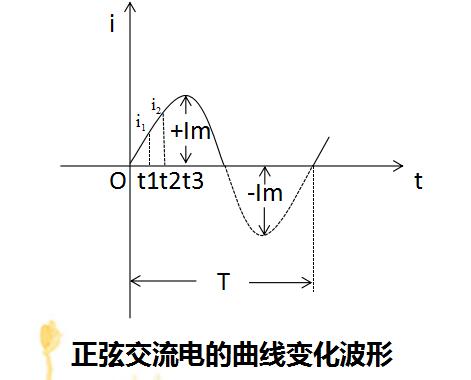
(1) The maximum value (also called peak value or amplitude), expressed by Em, Um, and Im.
The maximum value is the maximum instantaneous value. A positive value and a negative value must appear twice in a cycle.
(2) Angular frequency
Generally, the angle of the sinusoidal alternating current at any moment is called the electrical angle, and the electrical angle for each change is 360°, which is also called 2π radians. Angular frequency is the radians of the sinusoidal alternating current in seconds, expressed in symbols, and the unit is radians per second, expressed in rad/s. Because the radians of alternating current is 2π, the radians of alternating current with frequency f are 2πf in one second, and the angular frequency can be expressed as: ω=2πf.
(3) The initial phase and the phase difference φ, φ1-φ2.
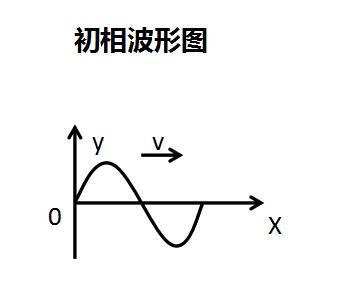
The initial phase is the phase of the sine at the starting time. On the waveform diagram, the initial phase is defined as the angle between the starting point of the positive half wave and the origin of the coordinates. When φ=0, the starting point of the positive half-wave just falls on the origin O; when φ>0, the starting point of the positive half-wave is on the left of the origin O; when φ<0, the starting point of the positive half-wave is on the right of the origin O.
Phase difference refers to the difference between the phase (or initial phase) of two sinusoids of the same frequency. The phase difference between two sinusoidal alternating currents of the same frequency has nothing to do with time. Therefore, it is meaningless to discuss the phase difference between two sine quantities of different frequencies.
When analyzing AC circuits, it is often necessary to compare the phase relationship between several sine quantities of different frequencies. At this time, you can choose the initial phase zero of a sine quantity as the reference sine quantity, and the other quantities can be compared with the reference sine quantity. To determine its initial phase, it cannot be changed during the discussion.
Characteristics of sinusoidal alternating current1. The AC voltage is easy to change.
In the power system, the application of transformers can easily change the voltage, high-voltage transmission can reduce the loss on the line; reduce the voltage to meet the voltage level of different electrical equipment.
2. The structure of the AC generator is simpler than that of the DC generator.
Fast Charging Power Bank,Light Data Cable,Portable Power Station,Mobile Power Bank,Digital Display Power Bank Charger
Pogo Technology International Ltd , https://www.wisesir.net
