The basic operation mode of the stepper motor is called "excitation mode", which can make the stepper motor work in full-step mode, half-step mode and micro-step mode. The micro-step mode can effectively reduce the noise of the phase current of the stepper motor. Improve the inherent noise and vibration problems of stepper motors. Three excitation modes will be introduced below.
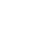 Full-step mode
Full-step mode
The so-called full-step mode is designed to work at a fixed step angle based on the inherent structure of the motor. With one electric pulse, the stepping motor advances by one step angle. This step angle is determined by the design structure of the motor, and can also be understood as the motor rotating at the maximum step angle.
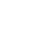 Half-step mode
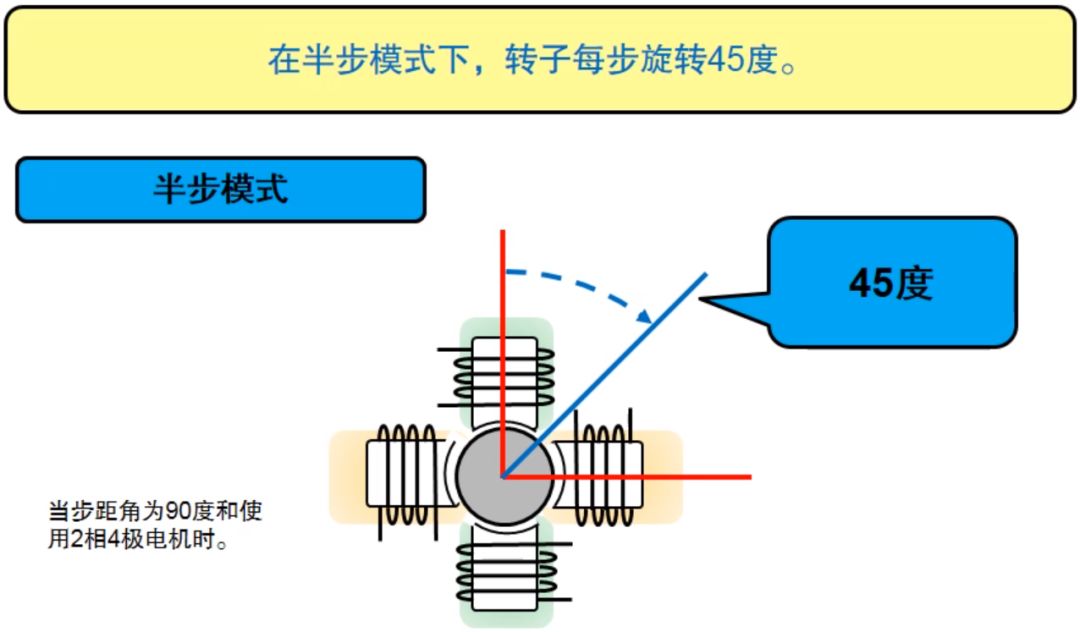
Half-step mode
Half-step mode is to perform step rotation at half the step angle determined by the inherent structure of the motor. As shown in the figure below, the total number of poles of the stepper motor is 4 levels, and the corresponding step angle is 90 degrees, then in the half-step mode, the stepper motor rotates 45 degrees per pulse.
 Microstep mode
Microstep mode
The micro-step mode is similar to the half-step mode, with a smaller step angle, that is, 1/4 step, 1/8 step, and 1/16 step, which can reach very high subdivisions. The corresponding step angle is the whole step step angle multiplied by the microstep coefficient.
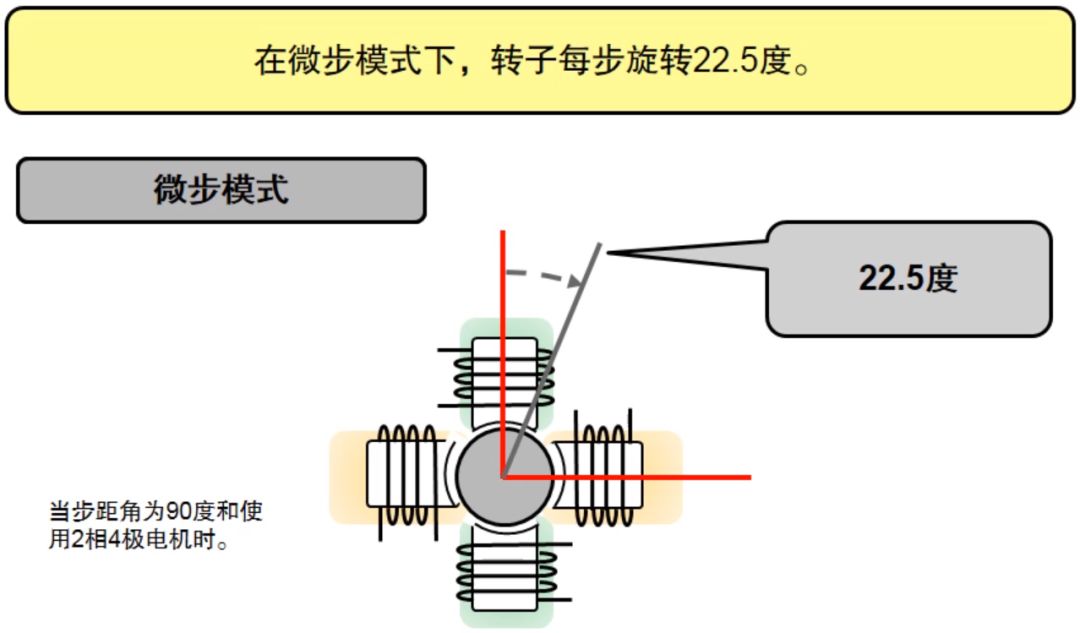
The smaller the step angle of the stepping motor, the higher the machining accuracy required, and the greater the error of the step angle during the corresponding micro-step.
Motor control driver
The stepper motor cannot be directly connected to the power frequency AC or DC power supply, but must use a dedicated stepper motor driver, which consists of a pulse generation control unit, a power drive unit, and a protection unit. As shown below.
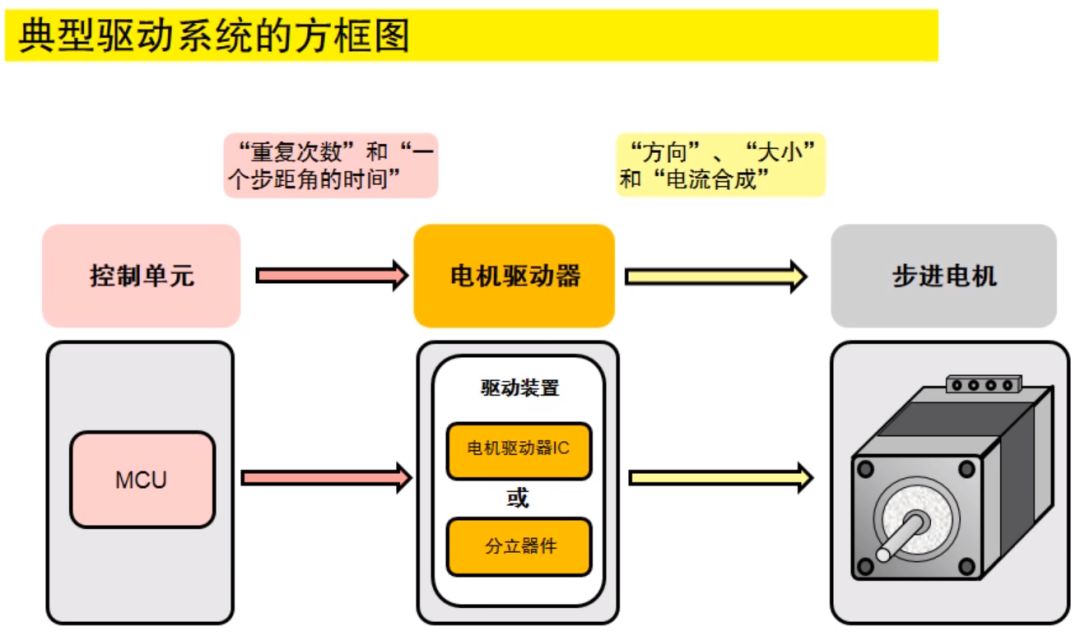
The drive unit is directly coupled with the stepper motor, which can also be understood as the power interface of the stepper motor microcomputer controller. The following will illustrate the system using MCU and separate components. The MCU is equivalent to the brain that controls the motor. It sends the step angle time, rotation direction and number of repetitions of the motor to the discrete device. The discrete device amplifies the voltage and current according to the signal sent by the MCU and sends them to the motor to drive The motor rotates.
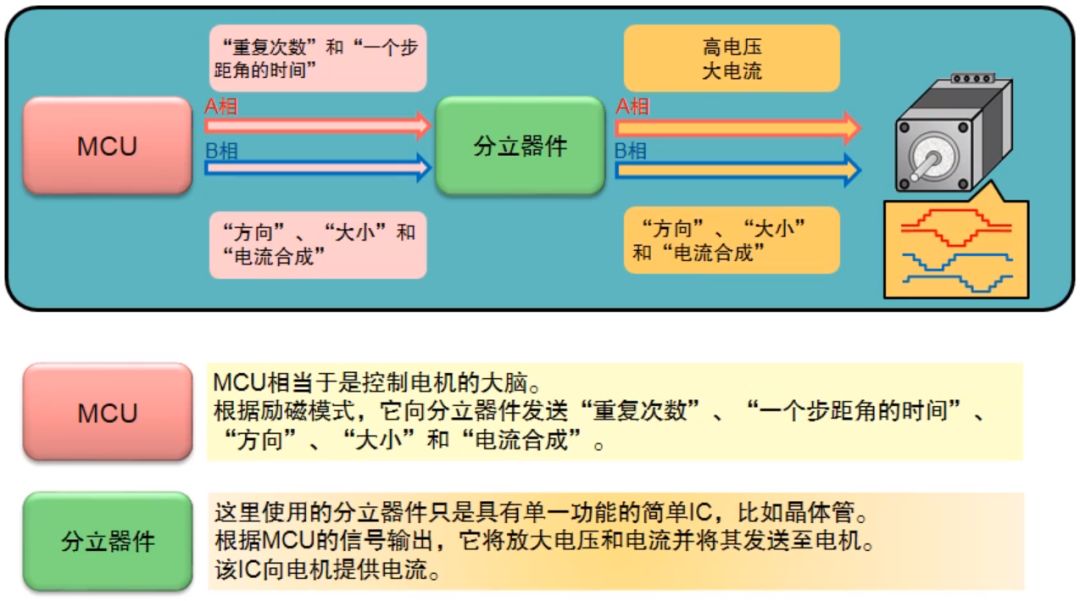
As shown in the figure above, the system uses MCU and motor control driver IC. From the input control signal to distinguish, stepper motor controller IC can be divided into phase input type and clock input type. The phase input type means that the current direction of each excitation phase of the motor is controlled by the input signal, while the clock input type means that the drive of the motor is controlled by the pulse signal.
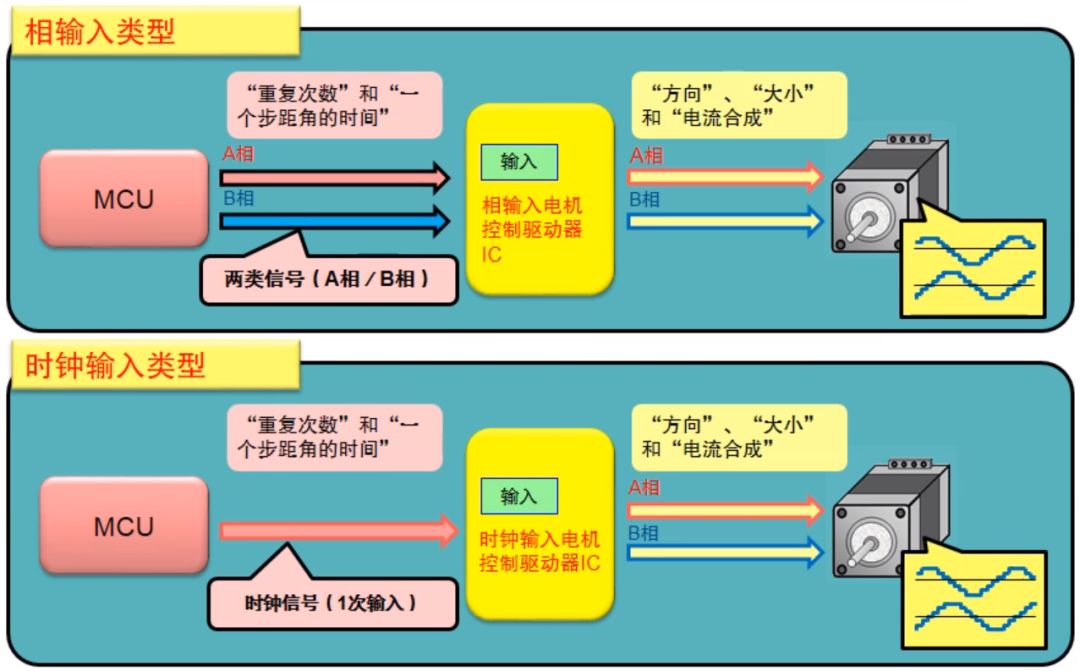
Phase force
The phase-in motor driver needs two-phase control signals of A and B, only the clock signal, and the MCU that needs the control signal does more transportation work.
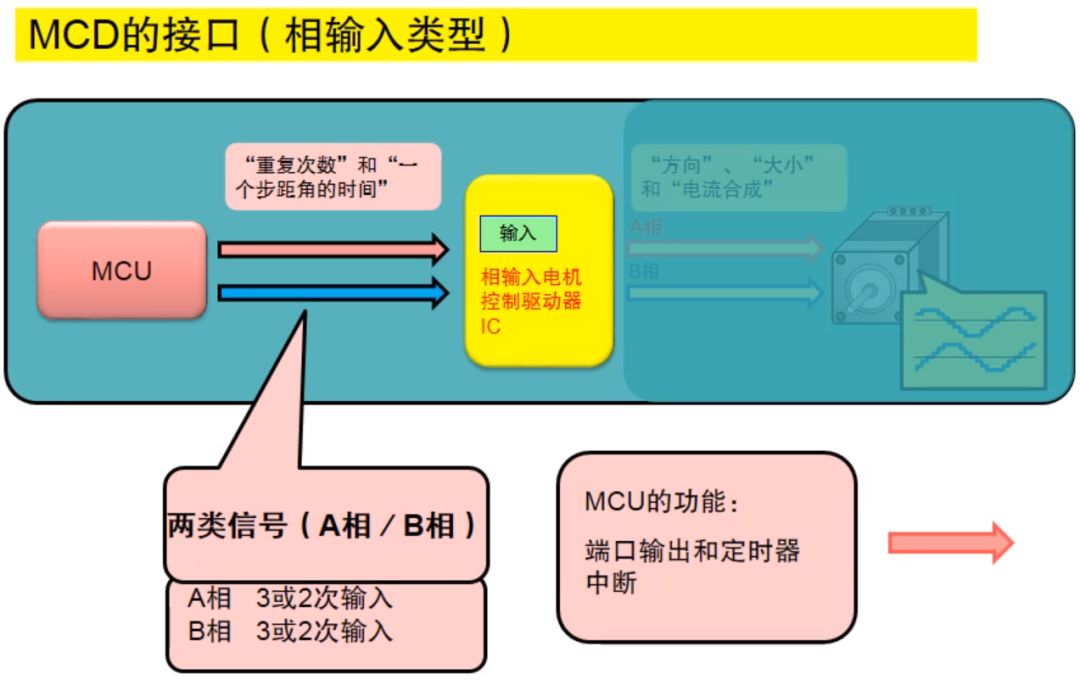
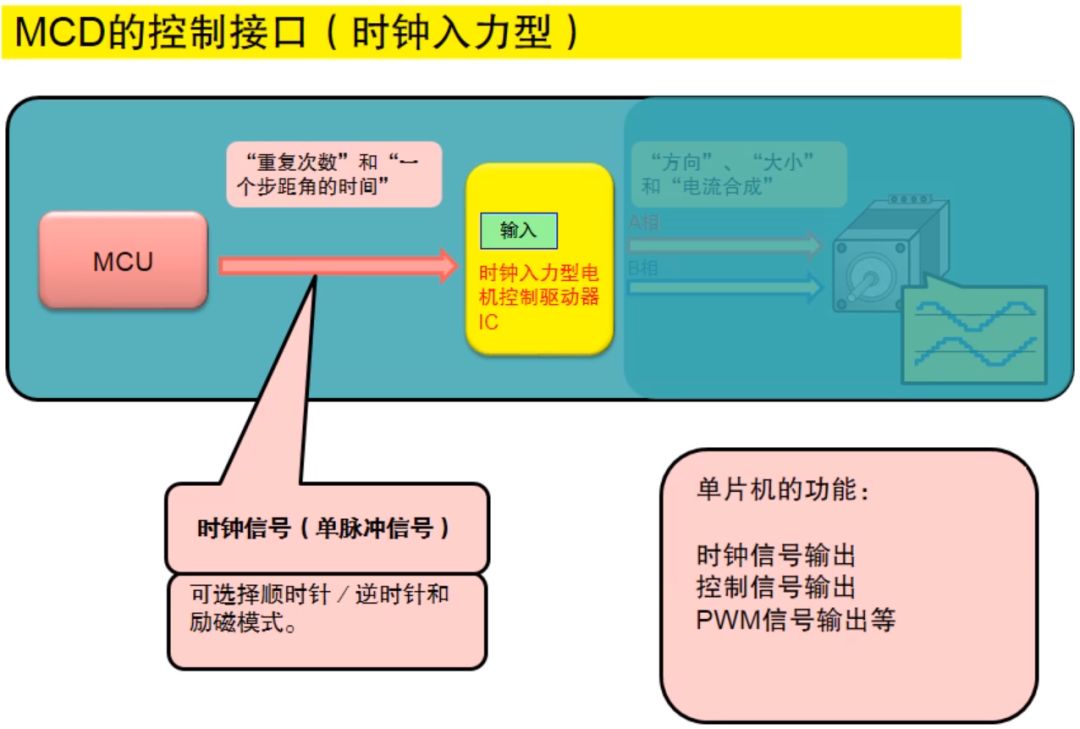
Clock input type
The control interface of the clock input type motor driver needs a clock signal (single pulse signal) input, and its control signal is relatively simple, and the MCU takes up less resources.
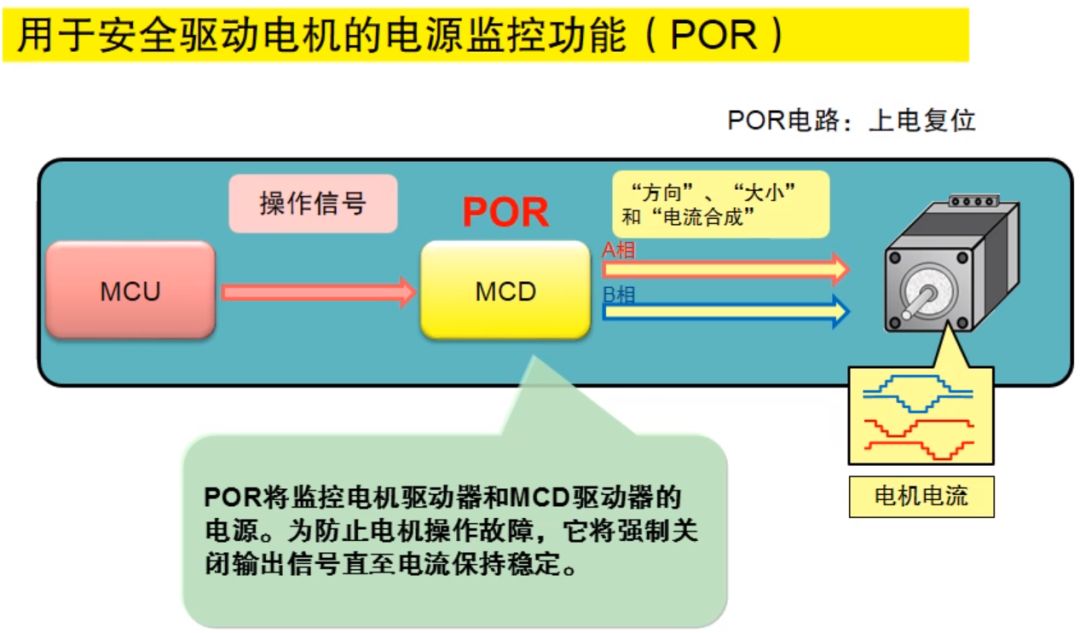
Motor drive safety technology
Power-on reset function (POR)
The power-on reset function will monitor the motor drive and the power supply of the motor drive controller. In order to prevent the motor from malfunctioning, it will forcibly turn off the output signal until the supply voltage remains stable. As shown below.
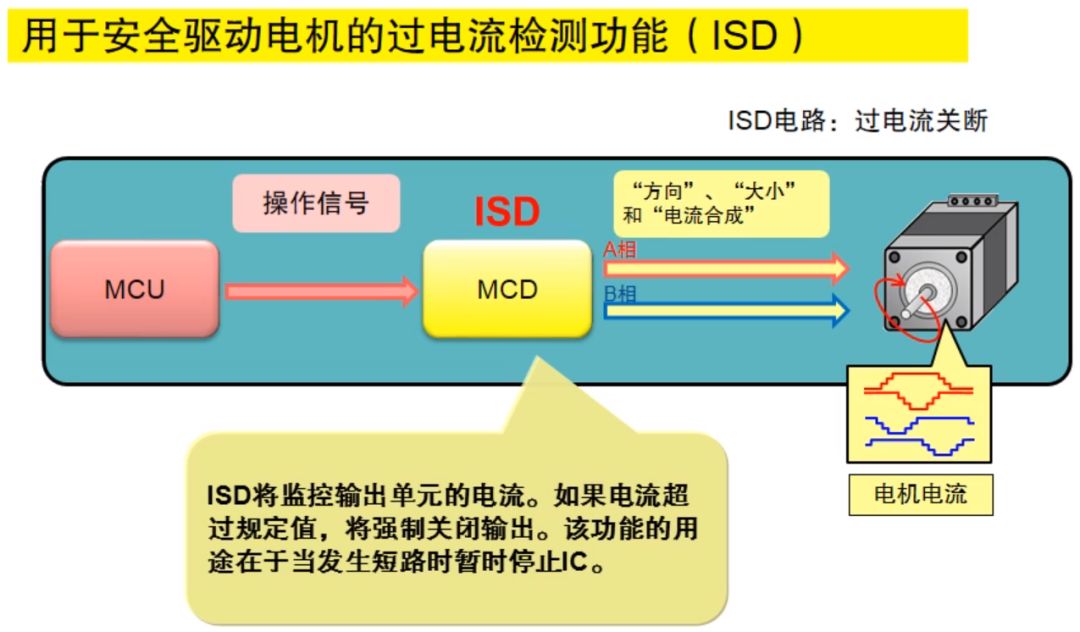
Overcurrent detection function (ISD)
The overcurrent shutdown function will monitor the current of the output unit, and if the current exceeds the specified value, the output will be forcibly turned off. The purpose of this function is to temporarily stop the IC output when a short circuit occurs. As shown below.
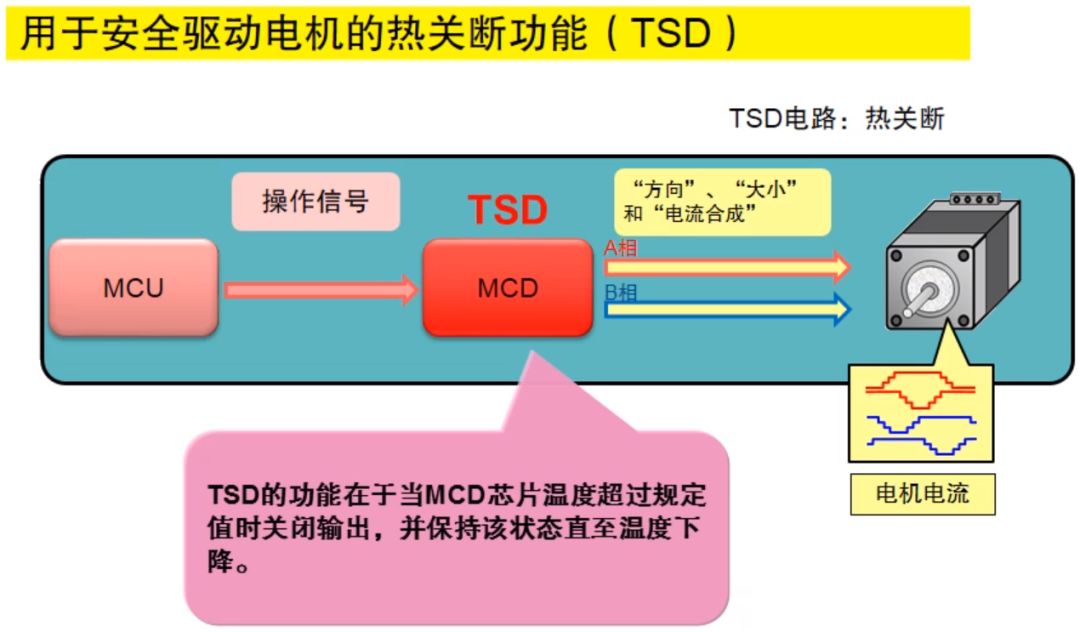
Thermal shutdown function (TSD)
The thermal shutdown function is to turn off the output when the temperature of the motor control driver chip exceeds a specified value, and maintain this state until the temperature drops.
General Purpose Servo Motors,Cnc Lathe Electric Motors,Cnc Lathe Servo Motor,Servo Motor For Sewing Machine
Zhejiang Synmot Electrical Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.synmot-electrical.com
