The automobile engine cooling system is one of the six major systems of the engine. Its function is to dissipate part of the heat absorbed by the heated parts in time to ensure that the engine works at the optimum temperature.
The role of the car engine cooling system
The purpose of establishing a cooling system in a car is to keep the engine operating at the proper temperature.
After the combustion of the mixture in the engine combustion chamber, high-temperature and high-pressure gas (about 800-2000 ° C) is generated. Therefore, the cylinder must be cooled, otherwise the moving parts are thermally expanded to break the normal gap, the mechanical strength is reduced and damaged, and the lubrication fails and is stuck.
If the cooling is excessive, the cylinder charge will decrease, the combustion will be abnormal, the power will decrease, the fuel consumption will increase, and the lubrication will be poor.
When the engine is working, the temperature of the gas in the cylinder can be as high as 1727~2527C. If it is not cooled in time, the temperature of the engine parts will be too high, especially the parts that are in direct contact with the high-temperature gas will affect the normal matching gap due to thermal expansion. The moving parts are blocked or even stuck. In addition, the high temperature also causes the mechanical strength of the engine parts to drop, causing the lubricating oil to lose its effect. The main function of the cooling system is to dissipate part of the heat absorbed by the heated parts in time to ensure that the engine works at the optimum temperature. The cooling system can be divided into air-cooling and water-cooling depending on the cooling medium. If the heat of the high-temperature parts in the engine is directly dissipated into the atmosphere, the cooling device is called an air-cooling system. The device that transfers the heat to the cooling water first and then to the atmosphere for cooling is called a water cooling system. Due to the uniform cooling of the water cooling system, the effect is good, and the engine running noise is small. Currently, the water cooling system is widely used in automobile engines.
Automotive engine cooling system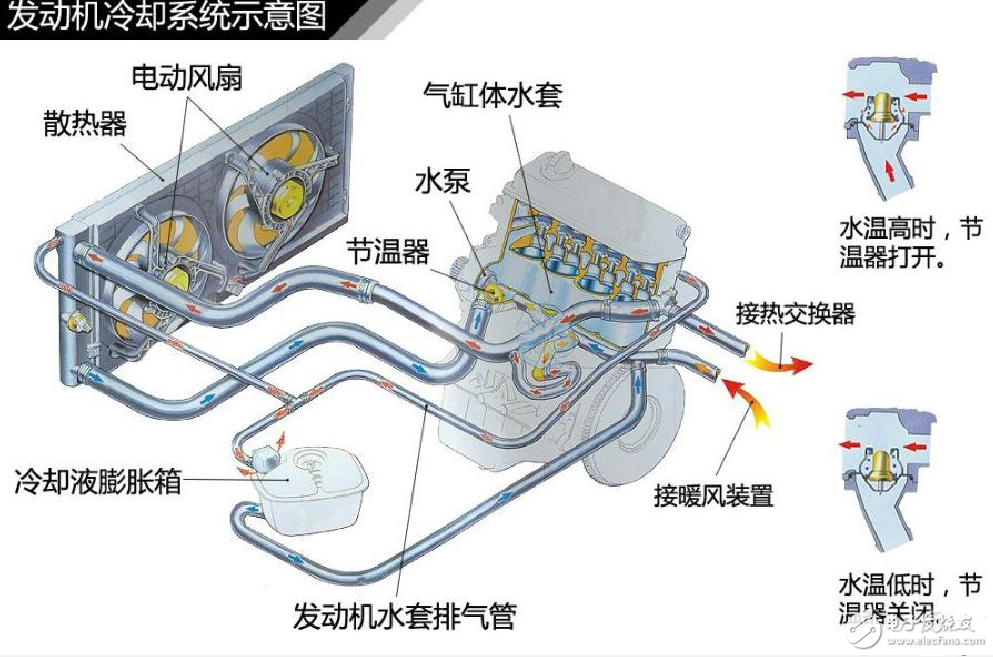
In the entire automotive engine cooling system, the cooling medium is a coolant, and the main components are a thermostat, a water pump, a water pump belt, a radiator, a cooling fan, a water temperature sensor, a liquid storage tank, and a heating device (similar to a radiator).
1) Coolant
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, is a liquid consisting of antifreeze additives and additives that prevent rust from metals and water. It requires antifreeze, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity and deteriorating properties. Ethylene glycol is often used as the main component, and antifreeze added with anti-corrosion and water is added. The water for the coolant is preferably soft water, which prevents the scale of the engine water jacket from generating scale, causing heat transfer to be blocked and the engine to overheat. Adding antifreeze to the water while increasing the boiling point of the coolant can play an additional role in preventing premature boiling of the coolant. In addition, the coolant also contains a foam inhibitor, which can suppress the generation of foam under the agitation of the water pump impeller and hinder the heat dissipation of the water jacket wall.
2) Thermostat
From the introduction of the cooling cycle, it can be seen that the thermostat is determined to go "cold cycle" or "normal cycle". The thermostat is turned on after 80 ° C, and the opening is maximum at 95 ° C. The thermostat cannot be turned off, causing the cycle to enter the "normal cycle" from the beginning, which causes the engine to fail to reach or reach normal temperatures as quickly as possible. The thermostat cannot be turned on or turned on, which makes the coolant unable to circulate through the radiator, causing the temperature to be too high or normal when the time is high. If the overheating occurs due to the thermostat not being turned on, the temperature and pressure of the upper and lower water pipes of the radiator will be different.
3) Water pump
The function of the pump is to pressurize the coolant to ensure it circulates in the cooling system. The failure of the water pump usually causes leakage of the water seal, and the bearing fault causes the rotation to be abnormal or sound. In the event of engine overheating, the first thing to notice is the pump belt to check if the belt is broken or loose.
4) radiator
When the engine is working, the coolant flows in the radiator core, the air passes outside the radiator core, and the hot coolant cools due to heat dissipation to the air. There is also an important small part on the radiator, which is the radiator cover, which is easily overlooked. As the temperature changes, the coolant will “swell and contractâ€, and the internal pressure of the radiator will increase due to the expansion of the coolant. When the internal pressure reaches a certain level, the radiator cover will open and the coolant will flow to the reservoir; Lower, the coolant flows back into the radiator. If the coolant in the reservoir does not decrease and the level of the radiator is reduced, then the radiator cap will not work!
5) Cooling fan
During normal driving, the high-speed airflow is sufficient to dissipate heat, and the fan generally does not work at this time; however, when running at slow speed and in situ, the fan may rotate to assist the radiator to dissipate heat. The start of the fan is controlled by a water temperature sensor.
6) Water temperature sensor
The water temperature sensor is actually a temperature Switch. When the engine inlet water temperature exceeds 90 °C, the water temperature sensor will turn on the fan circuit. If the cycle is normal and the fan does not turn when the temperature rises, the water temperature sensor and the fan itself need to be checked.
7) Liquid storage tank
The function of the liquid storage tank is to supplement the change of the cooling liquid and the buffer "thermal expansion and contraction", so do not overfill the liquid. If the reservoir is completely empty, you can't just add liquid to the tank. You need to open the radiator cover to check the liquid level and add coolant. Otherwise, the tank will lose its function.
8) Heating device
The heating device is in the car and generally is not a problem. It can be seen from the introduction of the cycle that this cycle is not controlled by the thermostat, so the heating is turned on when the vehicle is cold. This cycle has a slight delay on the temperature rise of the engine, but the impact is not so great, and there is no need to heat up the engine. Let people freeze. It is also because of the characteristics of this cycle that in the emergency situation where the engine is overheated, the window is opened and the heating is opened to the maximum, which will help the engine to cool down.
Switch
Position Selector Switch,Rotary Selector Switch,Pole Rotary Switches,Ceramic Rotary Switch
Foshan City Jiulong Machine Co., Ltd , https://www.jlthermostat.com
